Dual boot vs. Virtualization: Which is best for running multiple operating systems?
Do you primarily use Windows 11 but want to have a quick look at a Linux distribution like Linux Mint? Well, booting from a live DVD or USB stick is a convenient solution. The advantage of this is that nothing needs to be installed, and your Windows configuration remains unchanged. When you remove the DVD or USB stick, your PC will restart normally into its installed operating system.
Live system: Start Linux Mint from a USB stick or DVD to try it out without making any changes to your PC.
IDG
If you want to have the full Linux Mint experience, then a virtual computer is the way to go.
A virtual computer behaves more or less like a real PC, allowing you to exchange data with the host system (usually your Windows computer) or other devices in the network. However, since virtual Windows or Linux guests are isolated from the host and network by default, it’s primarily suitable for software tests and surfing potentially dangerous websites.
One major advantage is the ability to freeze the system and restore it to a previous backup with a single click. Another option is the parallel installation of two or more operating systems on a hard drive or SSD, otherwise known as multibooting.
Installation: If Linux Mint is installed in parallel with Windows, select the desired system when booting.
IDG
Once you’ve booted up the PC, select the operating system in the boot manager. This lets you use Windows 11 and Linux Mint at the same time, allowing you to access stored data whether it’s on your local drive or a network share.
For an in-depth look at how virtualization works, check out our guide here.
Advantages and disadvantages of virtual PCs
Virtualization technology has been a part of everyday life in company networks and data centers since the 2000s. It allows the number of dedicated computers to be reduced and the existing hardware to be optimally utilized. Many other virtual servers can run independently of each other on a host server, which ultimately saves energy and administration costs.
For home users, desktop virtualization solutions offer a sophisticated way of testing different operating systems, using Linux under Windows or even Windows under Linux without a large PC base.
The biggest advantage of virtualization is that you always have a clean guest system, no matter what you do with it. Ideally, your host system remains completely untouched in the event of accidents and infections in the virtual machine. You can also make changes to the settings within the virtual machine to your heart’s content. With one click, you can return to the original state. On a real PC, a major crash can result in costly repair work. That said, virtualization has its limits.
Virtual PC: Whether live system or installation – Linux Mint runs isolated in a Virtualbox environment.
IDG
While virtualization environments can translate the commands of the guest operating system to CPUs and memory with little loss of speed, this is not so easy with other hardware components. The graphics performance is not sufficient for complex games, as the memory is usually limited to 128 MB in the virtualization software, even if much more is available.
Advantages and disadvantages of multiboot
With a multiboot setup–whether with a live system or a permanently installed operating system–you can take advantage of your PC’s resources. The processor, RAM, and graphics memory are available without restriction. The same goes for other hardware components such as the printer, webcam, and scanner.
A multi-boot system can be used in combination with Windows 11 and Linux Mint, for example, if the installation of Windows 11 fails due to the lack of hardware requirements. It also allows you to divide different tasks, effectively keeping work and personal use separate on the same machine. However, the disadvantage here is the double administration effort. 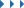
© 2025 PC World 0:35am  
|
|
|
 |
|